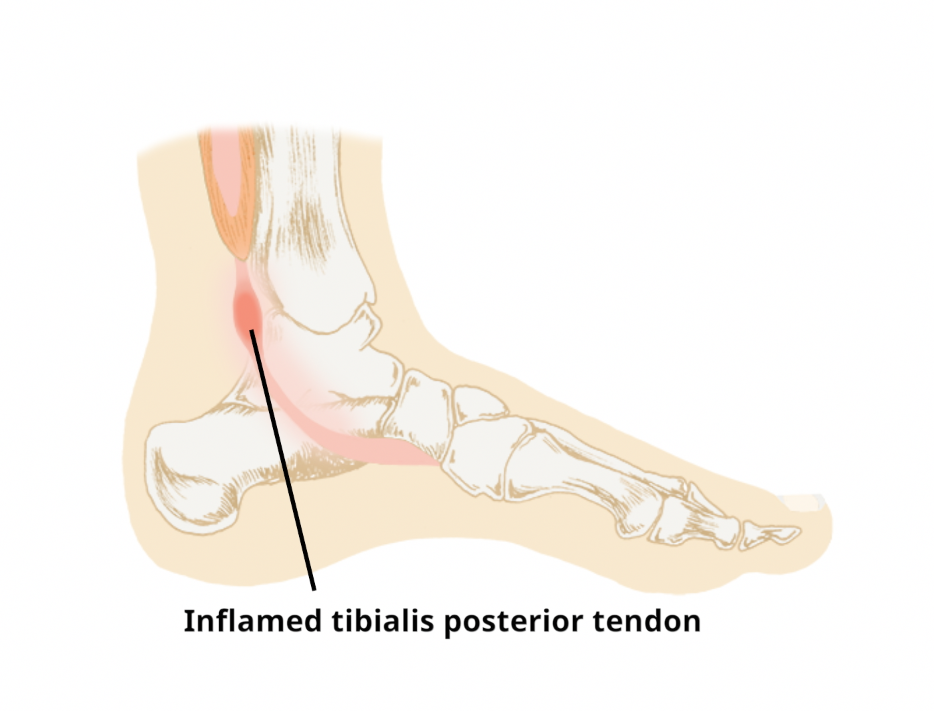
 Tibialis posterior dysfunction is a condition causing pain over the inside of the lower calf and ankle. It arises when the tibialis posterior tendon is unable to provide sufficient support to the arch of the foot.
Tibialis posterior dysfunction is a condition causing pain over the inside of the lower calf and ankle. It arises when the tibialis posterior tendon is unable to provide sufficient support to the arch of the foot.
It is often due to a tear or a generalised weakening and elongation of the tendon. Sometimes the tendon itself remains intact but the problem is caused by significant inflammation of the sheath which surrounds the tendon. In this case, the problem can be referred to as a tenosynovitis. Individuals with an inherently flat foot posture (which places the tibialis posterior under greater load) are particularly vulnerable to developing a tear or elongation to the tendon.
How is a tibialis posterior dysfunction treated?
Initial Management
It is usually necessary to rest, or at least reduce the amount of activity, for a short while to help the symptoms settle. Applying an ice pack for 5-15 minutes every 2-3 hours may provide some relief. You may wish you try over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol if needed.
Exercises
Once the acute pain has settled, a tibialis posterior dysfunction can be managed effectively by adhering to the following advice and exercise routine to strengthen the tibialis posterior muscle and tendon.
Footwear
You should ensure that you use well-fitting, supportive footwear with adequate arch support, both during your everyday activities and, particularly, during exercise. Very flat shoes and high heels can also exacerbate the problem. Orthotic inserts placed inside your shoes can ensure better foot position, which should prevent the problem recurring.
Further options
If there is a severe tear or rupture, total rest in a cast or boot may be required.
Surgical management
Surgical repair is occasionally considered in severe cases.